Indoor Radon Gas Exposure Is the Leading Cause of Lung Cancer Second Only to Smoking
 February 16, 2011
February 16, 2011  Kyriaki (Sandy) Venetis
Kyriaki (Sandy) Venetis 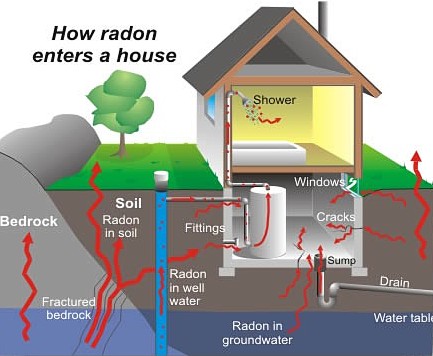 Graphic courtesy of the World Health Organization.
Graphic courtesy of the World Health Organization.
Several federal agencies are planning to meet sometime by the end of this month to discuss measures for reducing radon risk in housing and buildings that they either operate or regulate.
Last November, agencies that included the U.S. Environmental Protection (EPA), the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), and the U.S. Veterans Administration (VA) met for a Federal Radon Summit to address growing concern over potentially high levels of radon.
Right now, homes and buildings operated and regulated by government agencies are not required to undergo mandatory testing for radon, and HUD doesn’t require radon testing of homes that are being insured under the U.S. Federal Housing Administration (FHA) mortgage insurance program.
The concerns come because the EPA now calculates that, “Nearly one out of every 15 homes in the United States is estimated to have elevated radon levels,” in its Citizens Guide to Radon.
Radon is a colorless and odorless radioactive gas. It comes from naturally decaying uranium, which is found in most soil. The way that radon gets into a home or building space is that it travels up through the ground to the air above and enters through cracks or holes in the foundation.
When trapped indoors, radon builds up and the problems begin. The EPA estimates that about 21,000 annual lung cancer deaths are radon related. The agency also found that indoor radon increases the risk of a smoker developing lung cancer.
